
Addiction definition is a chronic condition where individuals compulsively seek and use substances despite harmful consequences. It affects brain function and behavior.
Addiction impacts millions globally, leading to serious health and social issues. It involves a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. Substances like drugs, alcohol, and even behaviors like gambling can trigger addiction. The brain’s reward system becomes hijacked, creating an intense craving and loss of control.
Early intervention and treatment are crucial for recovery. Support systems, therapy, and sometimes medication can help manage addiction. Awareness and education play vital roles in prevention and reducing stigma. Understanding addiction as a medical condition is essential for compassionate and effective treatment.
Addiction And Its Core Elements
Addiction is a complex condition affecting the brain and behavior. It creates a strong craving for substances or activities. Understanding its core elements helps us grasp its impact.
Psychological Aspects
Psychological aspects play a crucial role in addiction. Mental health issues like anxiety and depression often contribute to addiction. These conditions make individuals more prone to substance use. Stress and trauma also have a significant impact.
People use substances to cope with difficult emotions. Cognitive distortions influence their behavior. They may believe substances help them feel better. Over time, these thoughts reinforce the addiction cycle.
Physical Aspects
Physical aspects of addiction involve changes in the body. Tolerance is a key element. Over time, the body needs more of the substance to achieve the same effect. Withdrawal symptoms occur when the substance is not used.
These symptoms can be severe and include nausea, shaking, and sweating. Brain chemistry also changes. The reward system becomes altered. This makes it hard to experience pleasure without the substance.
Genetics can play a role in physical addiction. Some people are more likely to develop an addiction due to their genetic makeup.
Types Of Addiction
Addiction can take many forms and affect people in different ways. Understanding the types of addiction can help in recognizing the signs and finding appropriate treatment. Addictions are generally categorized into two main types: Substance Addiction and Behavioral Addiction.

Substance Addiction
Substance addiction involves the use of drugs or alcohol. These substances change the brain’s chemistry, leading to dependency. Common examples include:
- Alcohol – Excessive drinking can lead to addiction.
- Narcotics – Drugs like heroin and prescription painkillers.
- Stimulants – Cocaine, methamphetamine, and certain prescription medications.
- Nicotine – Found in cigarettes and vaping products.
People with substance addiction may experience withdrawal symptoms. These symptoms can be physical or emotional.
Behavioral Addiction
Behavioral addiction involves compulsive behaviors rather than substances. These behaviors can be just as harmful. Common examples include:
- Gambling – Compulsive betting on games or sports.
- Internet – Excessive use of social media, gaming, or browsing.
- Shopping – Uncontrollable buying of items.
- Eating – Overeating or unhealthy eating patterns.
Behavioral addictions often impact relationships and daily life. They can cause significant stress and anxiety.
Recognizing these types of addiction is the first step to getting help. Treatment options vary, but support is always available.
Symptoms Of Addiction
Understanding the symptoms of addiction is crucial. Recognizing these signs early can help provide timely support. Addiction can manifest in various ways, affecting both the body and mind.
Physical Symptoms
Addiction often leads to noticeable physical changes. These changes can be a warning sign that someone needs help.
- Weight loss or gain: Rapid changes in weight can occur.
- Bloodshot eyes: Eyes may appear red or glazed.
- Poor hygiene: Neglecting personal care is common.
- Sleeping problems: Insomnia or excessive sleeping may happen.
- Tremors or shakes: Uncontrolled shaking can be a sign.
Emotional Symptoms
Emotional changes are another key indicator of addiction. These can affect relationships and daily life.
- Mood swings: Sudden and extreme changes in mood.
- Depression: Feelings of sadness and hopelessness.
- Anxiety: Constant worry or fear.
- Isolation: Withdrawing from friends and family.
- Irritability: Becoming easily annoyed or angry.
Causes Of Addiction
Understanding the causes of addiction is crucial. Many factors contribute to addiction. The main causes can be divided into two categories: genetic and environmental.

Genetic Factors
Genetic factors play a significant role in addiction. If someone has a family history of addiction, they are more likely to develop an addiction. Genes influence how the brain responds to drugs and alcohol. Some people have a higher risk due to their genetic makeup. This risk can be inherited from parents or grandparents.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors also impact the likelihood of addiction. These factors include stress, peer pressure, and exposure to drugs. Living in an environment where drugs are available increases the risk. Social settings and relationships can also influence addiction. Friends or family members who use drugs can lead others to use them too.
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Genetic | Inherited risk from family |
| Environmental | Influences from surroundings |
- Family history of addiction
- Stressful life events
- Peer pressure
- Availability of drugs
Impact On Mental Health
Addiction deeply affects mental health. It changes the brain’s chemistry. This leads to many mental health issues. Two major impacts are anxiety and depression, and cognitive decline.
Anxiety And Depression
Addiction often leads to anxiety and depression. The brain’s reward system gets disrupted. This makes it hard to feel joy. People may feel anxious or depressed. Everyday tasks become overwhelming. These feelings can worsen over time.
Many people with addiction experience mood swings. They might feel happy one moment and sad the next. This emotional instability can affect relationships. Trust and communication break down. This adds to the mental health burden.
| Impact | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Anxiety | Restlessness, excessive worry, insomnia |
| Depression | Sadness, loss of interest, fatigue |
Cognitive Decline
Long-term addiction can cause cognitive decline. The brain’s ability to think clearly gets impaired. Memory issues are common. People may forget important details. They may also struggle with problem-solving.
Decision-making becomes difficult. People may make poor choices. Their judgment gets clouded by addiction. This can lead to risky behaviors. It also affects their daily life and responsibilities.
- Memory loss
- Difficulty concentrating
- Poor decision-making
These cognitive issues can last even after quitting substances. Early intervention is crucial. It helps reduce long-term damage. Support and therapy can aid recovery.
Impact On Physical Health
The impact of addiction on physical health is severe and wide-ranging. It affects many body systems and can lead to serious health issues. Understanding these impacts is crucial to grasping the full scope of addiction’s dangers.
Organ Damage
Substance abuse can cause significant damage to various organs. The liver is often the most affected, especially with alcohol and drug addiction. Chronic use can lead to liver cirrhosis, hepatitis, and liver failure. The heart is also at risk. Stimulants like cocaine and methamphetamine can cause heart attacks, arrhythmias, and hypertension. The lungs suffer from smoking-related substances. Chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and lung cancer are common outcomes.
Chronic Illnesses
Addiction often leads to chronic illnesses that require long-term care. Diabetes can develop from alcohol abuse due to its impact on insulin production. Kidney disease is a risk from both alcohol and drug abuse. Substance abuse weakens the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections and diseases. Mental health issues, like depression and anxiety, often accompany chronic physical illnesses caused by addiction.
| Organ | Possible Damage |
|---|---|
| Liver | Cirrhosis, hepatitis, liver failure |
| Heart | Heart attacks, arrhythmias, hypertension |
| Lungs | Chronic bronchitis, emphysema, lung cancer |
| Kidneys | Kidney disease |
Understanding these impacts underscores the importance of addressing addiction early. The longer the substance abuse continues, the greater the risk of irreversible damage to the body.
Societal Impact
Addiction affects more than just the individual. It impacts society. The ripple effects touch every corner of our lives. From the economy to legal systems, the consequences are extensive. Let’s explore the societal impact through key areas.
Economic Burden
Addiction places a heavy economic burden on society. Healthcare costs rise due to treatment and care. Productivity drops as people miss work. Businesses suffer losses. Governments spend more on public health and social services. A table can help illustrate these costs:
| Cost Type | Amount (in billions) |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | $120 |
| Lost Productivity | $200 |
| Criminal Justice | $60 |
| Social Services | $40 |
Crime And Legal Issues
Addiction often leads to crime. People may steal to support their habit. Violent crimes can increase. Drug trafficking grows. The legal system feels the pressure. Prisons become overcrowded. Courts handle more cases. Police resources stretch thin. Families and communities suffer. The cycle is hard to break.
- Theft and burglary rates rise.
- Violent crimes increase.
- More drug-related cases in court.
- Prison populations grow.
- Police resources are strained.
Stages Of Addiction
The stages of addiction describe the journey from initial use to full addiction. Understanding these stages can help in recognizing and addressing addiction early. Let’s explore each stage in detail.
Initial Use
Initial use is the first step in the addiction cycle. This is when a person tries a substance for the first time. It could be out of curiosity, peer pressure, or to relieve stress. During this stage, the brain experiences new sensations and may crave more.
Dependence
In the dependence stage, the body starts to need the substance. The person uses the substance regularly. They may notice they need more to get the same effect. This is called building a tolerance. Dependence can lead to physical and mental health issues.
Addiction
Addiction is the final stage. Here, the person cannot stop using the substance. It becomes their main focus in life. They may ignore work, family, and other responsibilities. Addiction can cause severe health problems. It also affects relationships and overall well-being.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Initial Use | First-time use, often due to curiosity or stress relief. |
| Dependence | Regular use, increased tolerance, physical and mental health issues. |
| Addiction | Inability to stop, affects life and health severely. |
Recognizing the stages of addiction can help in getting timely help. Early intervention can prevent the progression to full addiction. If you or someone you know is struggling, seek help immediately.

masscenterforaddiction.com
Diagnosis Of Addiction
Understanding the diagnosis of addiction is crucial in addressing this complex issue. Accurate diagnosis helps in creating effective treatment plans. This section delves into the essential aspects of diagnosing addiction.
Screening Tools
Several screening tools are used to identify addiction. These tools help in assessing the severity and impact of substance use. Commonly used tools include:
- Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) – Screens for alcohol addiction.
- Drug Abuse Screening Test (DAST) – Evaluates drug abuse severity.
- Brief Screener for Tobacco, Alcohol, and other Drugs (BSTAD) – Assesses multiple substances.
These tools are quick and easy to administer. They provide a preliminary indication of addiction, guiding further evaluation.
Clinical Assessment
A clinical assessment involves a detailed evaluation by a healthcare professional. This assessment includes:
- Medical History – Reviewing past and present health conditions.
- Substance Use History – Documenting the types and amounts of substances used.
- Mental Health Evaluation – Assessing for co-occurring mental disorders.
During the clinical assessment, healthcare providers use various methods, including:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Interviews | Structured or semi-structured conversations. |
| Questionnaires | Written forms completed by the patient. |
| Physical Exams | Checking for signs of substance use. |
Accurate clinical assessment is key to diagnosing addiction. It helps in formulating a personalized treatment plan.
Credit: m.youtube.com
Treatment Options
Understanding addiction is vital for effective treatment. Various treatment options exist to help individuals. Each approach offers unique benefits tailored to specific needs. Let’s explore these options.
Therapy And Counseling
Therapy and counseling are crucial in treating addiction. These methods help individuals understand their behaviors and triggers. There are different types of therapies available:
- Individual Therapy: One-on-one sessions with a therapist.
- Group Therapy: Sessions with others facing similar challenges.
- Family Therapy: Involves family members to support recovery.
Therapists use various techniques to aid recovery. These include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Focuses on changing negative thought patterns.
- Motivational Interviewing (MI): Enhances an individual’s motivation to change.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): Combines CBT with mindfulness techniques.
Medication
Medications can be effective in treating addiction. They help manage withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings. Common medications include:
| Medication | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Methadone | Reduces withdrawal symptoms for opioid addiction. |
| Buprenorphine | Helps reduce opioid cravings. |
| Naltrexone | Blocks the effects of alcohol and opioids. |
Doctors prescribe these medications based on individual needs. They monitor progress to adjust treatment as needed. Combining medication with therapy increases the chances of success.
Recovery Process
The recovery process from addiction is a journey. It involves several crucial steps to help individuals regain control. Each stage plays a vital role in fostering long-term sobriety.
Detoxification
Detoxification, or detox, is the first step. The body must remove harmful substances. This phase can be challenging. The body may react with withdrawal symptoms. Medical supervision is often needed. This ensures safety and comfort. Detox prepares the body for further treatment.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation follows detox. This step addresses the mind and behavior. There are two main types of rehab:
- Inpatient Rehabilitation: Patients stay in a facility. They receive 24/7 care. This setting provides structure and support.
- Outpatient Rehabilitation: Patients live at home. They visit the facility for treatment sessions. This option offers flexibility.
Rehabilitation includes several components:
- Therapy: Both individual and group therapy sessions.
- Education: Learning about addiction and coping strategies.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges.
Rehabilitation aims to build a foundation for a sober life.
Support Systems
Support systems play a crucial role in addiction recovery. They provide emotional and practical help. Here, we explore two key support systems: family support and support groups.
Family Support
It is vital for someone battling addiction. Family members offer emotional comfort. They help manage daily tasks. Their involvement boosts recovery rates.
Families can educate themselves about addiction. They can set healthy boundaries. They should stay positive. Open communication is key. It’s important to attend therapy together.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Emotional Support | Family provides love and understanding. |
| Practical Help | They assist with daily tasks and responsibilities. |
| Increased Recovery Rates | Involvement of family boosts the chances of recovery. |
Support Groups
Support groups offer a community of people who understand addiction. These groups meet regularly. They provide a safe space to share experiences.
Many people find support groups helpful. They feel less alone. They gain new coping strategies. There are different types of groups. Some are for specific addictions. Others are more general.
- Alcoholics Anonymous (AA)
- Narcotics Anonymous (NA)
- Smart Recovery
- Al-Anon Family Groups
Prevention Strategies
Preventing addiction is crucial for maintaining a healthy society. Effective strategies can help reduce the incidence of addiction. These strategies focus on education, awareness, and early intervention.
Education And Awareness
Education is a powerful tool for preventing addiction. Schools can teach students about the dangers of addiction. Parents can talk to their children about making good choices. Community programs can spread awareness through workshops and events.
Awareness campaigns can reach a broad audience. These campaigns can use social media, TV, and posters. They can highlight the risks and signs of addiction. This knowledge can empower people to make safer choices.
Early Intervention
Early intervention can stop addiction before it starts. Identifying risk factors early can help. These factors can include family history, mental health issues, and environmental influences.
Healthcare providers can screen for addiction risks during regular check-ups. Schools can offer counseling services for at-risk students. Community centers can provide support groups and resources.
Support systems are vital for early intervention. Families and friends can offer emotional support. Professional help can provide guidance and treatment options.
| Strategy | Action |
|---|---|
| Education | Teach the dangers of addiction |
| Awareness Campaigns | Use social media, TV, and posters |
| Early Screening | Identify risk factors during check-ups |
| Support Systems | Offer emotional and professional support |
Myths About Addiction
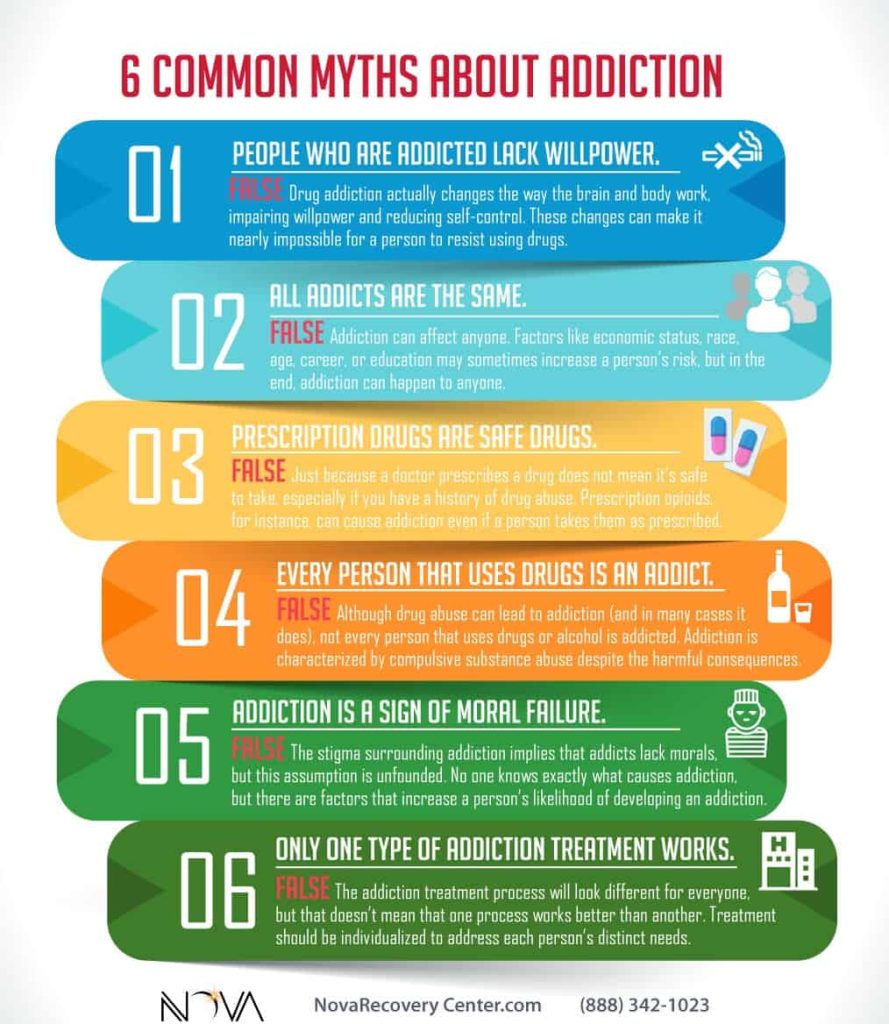
Addiction is often misunderstood. Many people hold onto false beliefs about it. These misconceptions can prevent people from seeking help. Understanding the truth about addiction can lead to better support and treatment.
goodtitevs.best
Misconceptions
Many believe that addiction is a choice. They think people can stop if they want. This is not true. Addiction changes the brain. It makes stopping very hard without help.
Another myth is that only certain people get addicted. Some think only weak or bad people suffer from addiction. In reality, anyone can develop an addiction. It does not matter your age, race, or background.
Some think addicts should just use willpower. They believe strong people can overcome addiction alone. Addiction is a disease. It often requires medical and psychological help.
Facts
Addiction affects the brain’s reward system. It changes how the brain works. This makes it hard to control urges and behaviors.
Treatment is available and can be effective. Many treatment options exist. These include therapy, medication, and support groups.
Addiction can be managed like other chronic diseases. With the right support, people can recover. They can lead healthy, fulfilling lives.
Early intervention can make a big difference. The sooner someone gets help, the better their chances of recovery.
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| Addiction is a choice. | Addiction is a disease. |
| Only certain people get addicted. | Anyone can develop an addiction. |
| Willpower alone can overcome addiction. | Addiction often needs medical and psychological help. |
Understanding these facts can help reduce stigma. It can encourage more people to seek help. Knowledge is a powerful tool in fighting addiction.
Future Of Addiction Treatment
The future of addiction treatment is transforming rapidly. New therapies and policies are leading this change. The aim is to offer better care and support for those in need.
Innovative Therapies
Innovative therapies are making a big difference in addiction treatment.
- Virtual Reality Therapy: Helps patients face their triggers in a safe environment.
- Neurofeedback: Teaches the brain to function more efficiently.
- Mindfulness-Based Therapy: Encourages patients to stay present and manage cravings.
These therapies offer new hope for those struggling with addiction.
Policy Changes
Addiction treatment policy changes are crucial for improving.
| Policy | Impact |
|---|---|
| Decriminalization of Drug Use | Reduces stigma and encourages treatment. |
| Increased Funding for Research | Leads to better therapies and understanding. |
| Insurance Coverage for All Treatments | Makes treatment accessible for everyone. |
These policies aim to improve access and quality of care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The True Meaning Of Addiction?
Addiction is a chronic condition where an individual compulsively seeks and uses substances or engages in behaviors despite harmful consequences.
What Is The Standard Definition Of Addiction?
Addiction is a chronic brain disorder. It involves compulsive seeking and use of substances despite harmful consequences. Behavioral changes, cravings, and loss of control are key symptoms. Treatment often requires medical and psychological interventions.
What Is The Legal Definition Of Addiction?
Addiction is legally defined as a chronic, relapsing disorder characterized by compulsive drug seeking, continued use despite harmful consequences, and long-lasting changes in the brain. It involves physical and psychological dependence on substances or behaviors.
What Is The Full Meaning Of Addicted?
Addicted means being physically or mentally dependent on a substance or activity, unable to stop despite harmful consequences.
Conclusion
Understanding addiction is crucial for tackling its impact on individuals and society. Recognizing the signs can lead to early intervention. Seeking help from professionals ensures the best chance for recovery. Stay informed and supportive to help those affected. Together, we can make a difference in addressing addiction effectively.
 Prevention from Suicide, Addiction, Narcotics and Pollution. Withdrawal and Recovery Facts of Narcotics | Symptoms of Suicidal thoughts & Ideations | Effects of Environment Pollution | Understand Addiction withdrawal
Prevention from Suicide, Addiction, Narcotics and Pollution. Withdrawal and Recovery Facts of Narcotics | Symptoms of Suicidal thoughts & Ideations | Effects of Environment Pollution | Understand Addiction withdrawal






